Speciation analysis. Solution for LC-IPC-MS
Sample introduction can be performed by nebulization of LC outflow, capillary electrokinetic chromatography (CEC), or CE, capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE). In addition, several modes of chromatographic separations can be used for species discrimination at preparative, capillary or nano scale, such as size exclusion chromatography (SEC), reverse phase (RP), ion exchange chromatography (IEC), hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) and affinity chromatography (AF).
Speciation analysis solution for LC-ICP-MS
In summary, HPLC separation, followed by ICP-MS detection is well established as the speciation analytical method of choice for many sample types and routine analysis laboratories. The instrumental configuration required for speciation analysis based on the use of LC-ICP-MS is made up of three clearly differentiated components:
- HPLC Instrument equipped with a specific column to species separation.
- Connection kit required to interface between HPLC and ICP-MS instruments.
- ICP-MS to selective isotopic detection system.

1. LC-ICP-MS: Speciation Analysis
The term “speciation analysis” is defined as the analytical activities of identifying and/or quantifying one or more individual chemical species in a sample. Since the growing awareness of the strong dependence of the toxicity of heavy metals upon their chemical forms has led to an increasing interest in the qualitative and quantitative determination of specific metal species, among which include arsenic (As), selenium (Se), mercury (Hg) and chromium (Cr). Speciation has therefore become an important topic of present-day analytical methodologies in routine analysis laboratories.
It is well known that the toxicity of elements depends upon their physicochemical forms. It has been well established that some metals and that metalloids (e.g., B, Si, Se) are essential for living organisms and that they are necessary components of some proteins and some metabolites playing important physiological functions. Their excess, as well as deficiency, may have serious consequences for living organisms. The species or chemical form, or oxidation state, of elements determines their mobility, bioavailability and toxicity. Since these properties vary greatly depending on the species in which an element is present, precise determination in environmental, clinical, food and agricultural samples and in consumer products is often essential to classify them.
Different techniques allow the separation and detection of element species. The coupling of liquid chromatography or ion chromatography for the separation of species and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) for detection is well established as a powerful technique. Thanks to its detection strength, ICP-MS enables the reliable determination of ultra traces of potentially harmful element species in a wide range of applications. Generally, speciation analysis plays a unique role in:
- Studies of biogeochemical cycles of chemical compounds.
- Determination of toxicity and ecotoxicity of selected elements.
- Quality control of food products.
- Control of medicines and pharmaceutical products.
- Technological and industrial process control.
- Research on the impact of technological installation on the environment.
- Examination of occupational exposure.
- Clinical analysis.
In this sense, the discrimination between specie is achieved with a separation device such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), capillary electrophoresis (CE) or gas chromatography (GC) which is coupled to a sensitive inductively coupled mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) to detect the metal present in the species moiety. The use of ICP-MS coupling to liquid chromatography (LC) is critical in speciation analysis since it allows: (i) multiisotopic metal analysis (including non-metals such as S, P, Se), (ii) high sensitivity, (iii) tolerance to matrix and, (iv) large linearity range. Several analyzers can be used in ICP-MS detection such as simple quadrupole (Q), triple quadrupole (QqQ), time of flight (TOF), sector field (SF) or multicollector (MC).
2. Solutions for your needs
For speciation analysis based on LC-ICP-MS analytical approach, Ingeniatrics Tecnologias S.L. has released to allow quick, reliable and easy connection of your LC to your ICP-MS, a specific one-piece connector for OneNeb® or MassNeb®, (one liquid inlet) with a 50 mm PEEK capillary to connect the exit of the chromatographic column directly to nebulizer (for high and low pressure, red and green PEEK capillary, respectively) (Figure 1A). In addition, in case of MultiNeb® nebulizer (two liquid inlets), the one-piece connectors designed for speciation analysis contains a 50 mm PEEK capillary to connect the exit of the chromatographic column directly to nebulizer and a second 50 mm PFA tubing (0.5 mm i.d.) (Figure 1B).
In speciation analysis based on the use of LC-ICP-MS, signal stability and plasma drift, also perturbations in the pressure LC pump, nebulization pressure alterations, nebulizer blockage, progressive clogging of the ICP-MS interface from total dissolved solids (TDS) contained in samples and mobile phase, changes in mobile phase composition causing perturbations on plasma signal response, especially when changing its composition during gradient elution and as result alterations on nebulization process efficiency and/or perturbations on the plasma ionization power related with modification in matrix composition and therefore in its chemical-physical properties (density, viscosity, solubility, and others), etc.
As a solution for your needs for your LC-ICP-MS approach, these Speciation Analysis High Pressure Connectors have been demonstrated in the following Application Notes, some advantages, such as resists blockage, fast washout, minimize dead volume and peak broadening (higher sensitivity and chromatographic resolution), principally in comparison with the conventional LC-ICP-MS connection kit employing for this purpose

Figure 1. A) Speciation Analysis Connector for HPLC-ICP using OneNeb® or MassNeb® Nebulizers (One Liquid Inlet)
B) Speciation Analysis Connector for LC-ICP using MultiNeb® Nebulizer (Two Liquid Inlets).

PEEK Tubing, Red, 0.005″ (0.13 mm) ID x 1/16″ OD – length 500 mm
PEEK Tubing, Green, 0.03″ (0.75 mm) ID x 1/16″ OD – length 500 mm
PFA Tubing, 0.02″ (0.50 mm) ID x 1/16″ OD – length 500 mm
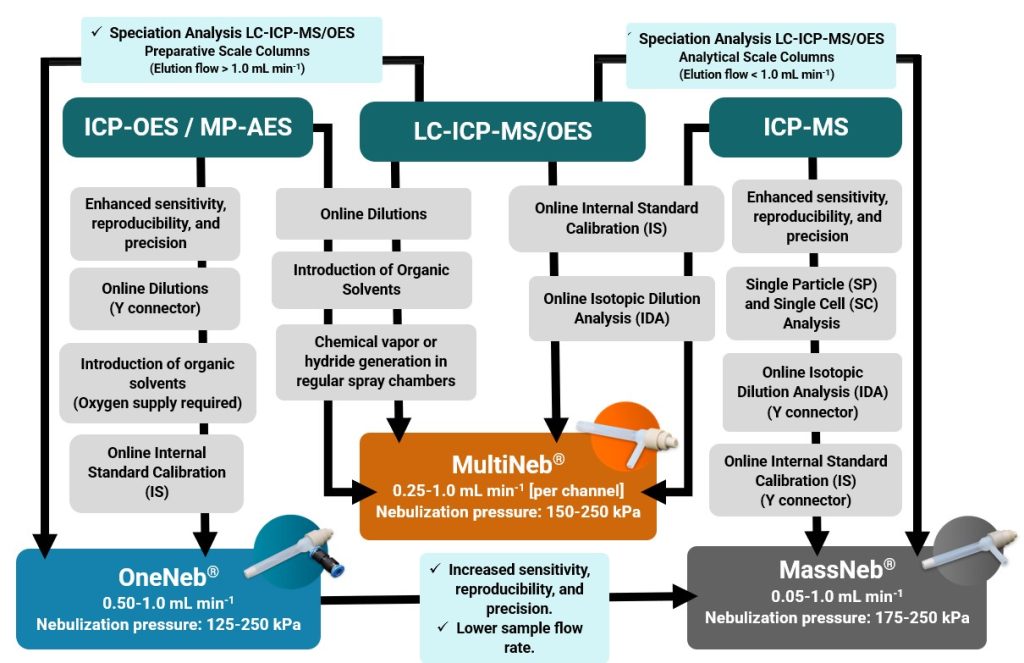
3. Analysis Nebulizer Selection for LC-ICP
Nebulizer selection is a critical but often overlooked aspect of ICP analyses. There are many different nebulizers available for ICP-OES and ICP-MS, for this reason, choosing the optimal one can be confusing and wrong selection. To achieve peak performance from your ICP analysis, it is essential to choose the optimal nebulizer based on your sample matrix and precision and limits sensibility required. In addition to any necessary accessories and analytical strategies to maintain long-term performance, such as humidifiers, ultrafiltration, hydride generation, etc.
In the last decade, nebulizer selection is challenging because there are many different types available. By far, concentric nebulizers are the most common type found on instruments today, as they generally provide the best performance. Even within the narrower category of concentric nebulizers, there is quite a range of designs. Ingeniatrics Tecnologías S.L. offers three models of nebulizers design of any manufacturer, with each model ideally suited to a variety of applications. Flow chart shown in Figure 2 was meant as a resource to help your laboratory select the best inert nebulizer to meet the performance requirement for speciation analysis by LC-ICP-MS.
Flow Chart for Nebulizer Selection using LC-ICP for Speciation Analysis

Figure 2. Flow Chart for Nebulizer Selection using LC-ICP for Speciation Analysis
4. Application Notes
4.1 Arsenic Speciation by HPLC-ICP-MS
MultiNeb®: Arsenic speciation in foods and human biological fluids using HPLC-ICP-MS by online internal standard correction technique.

In this liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (HPLC-ICP-MS) was optimized using an HPLC-ICP-MS to improve the analytical precision. For this purpose, we evaluate in this study the performance of MultiNeb® inert, robustness and durability nebulizer and a specific connector for speciation analysis designed by Ingeniatrics Tecnologías S.L. for analytical methodologies based on the use of HPLC-ICP-MS for speciation analysis.
Experimental
In speciation analysis based on the use of HPLC-ICP-MS, signal stability and plasma drift, also the perturbations in the pressure pump, nebulization process, nebulizer blockage and the mobile phase of HPLC might create some plasma perturbations, especially when changing its composition during gradient elution, etc. As a result, the detection response and the baseline signals often fluctuate during analysis, limiting precision and accuracy of quantifications. In this sense, with order to reduce the effects previously mentioned, in this work, an analytical methodology has been proposed for arsenic speciation analysis using HPLC-ICP-MS by online internal standard correction technique based on instrumental schematic representation of MultiNeb® based configuration showed in Figure 3 and operational conditions are shown in Table I.
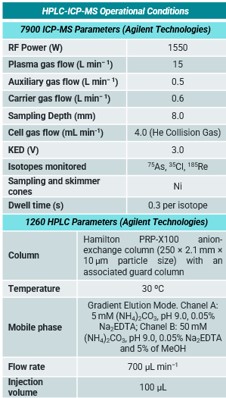
Table I. Operational conditions for 7900 ICP-MS and 1260 HPLC optimized for arsenic speciation
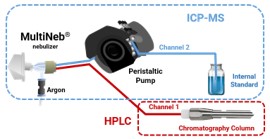
Figure 3. Schematic representation of MultiNeb® based configuration for Speciation Analysis using high-pressure connector for LC-ICP using MultiNeb® Nebulizer (two liquid inlets).
In addition, all five arsenic species were speciated under operational and experimental conditions optimized, previously described(Figure 4).

Figure 4. Chromatogram of five arsenic species speciated using HPLC-ICP-MS (10 ng mL−1 according to As for each form).
Results and Discussion
In this study, with order to reduce the effects previously mentioned, the fluctuations of 75AS and 185Re signals were investigated to confirm the efficiency of online internal standard quantification using 185Re as internal standard to reduce the deviations in the measurements. Additionally, a progressive increment in the baseline signal for both isotopes analyzed were obtained in all analysis, more pronounced in blank samples. Similar response was observed in the HPLC pressure pump along the elution time. This fact could be related with a gradient elution used for arsenic speciation analysis in this study. This observation was smoothing when the signal intensity ratios 75As/185 Re was represented.
Precision values were evaluated using different CRM, dogfish muscle (DORM-2), lobster hepatopancreas (TORT-3), rice (ERM-BC211), human urine and serum (Clinchek). The results obtained are shown in Table II. Chromatograms obtained are shown in Figure 5.

Table II. Experimental and certified mean values for total arsenic and arsenic species concentrations in the different foods and human biological fluids analyzed, as well as the RSD obtained for 2 replicates using HPLC-ICP-MS and 5 replicates for ICP-MS determination using MultiNeb® nebulizer by online internal standard calibration technique (Grey: certified values; Green: Experimental results).
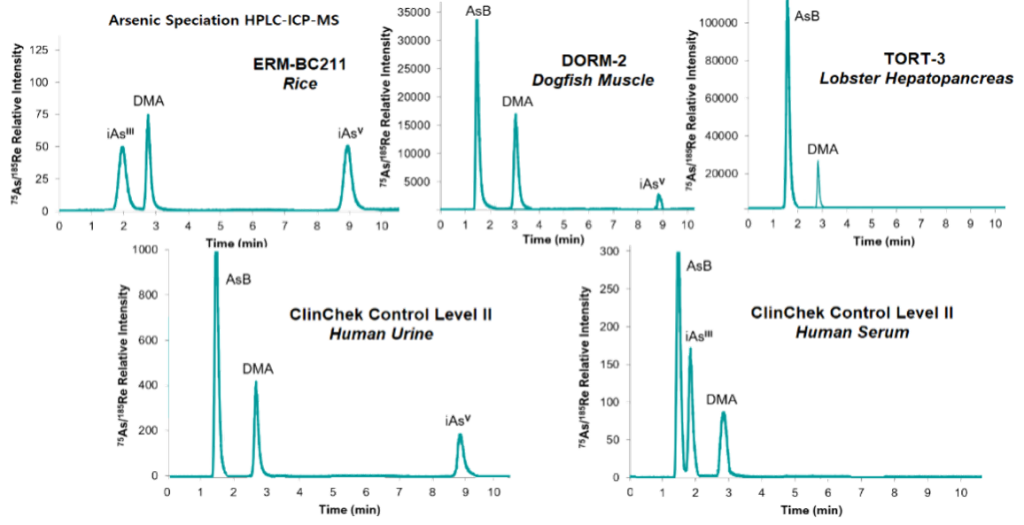
Figure 5. Chromatograms obtained by HPLC-ICP-MS with online internal standard calibration technique using MultiNeb® in different foods and human biological fluids analyzed in this study.
Conclusion: In this study, it has been demonstrated that the new MultiNeb® multiple nebulizer presents higher precision, sensitivity, signal stability and reproducibility in total arsenic determination using ICP-MS and arsenic speciation quantification based on HPLC-ICP-MS coupling by online internal standard calibration technique.
4. Application Notes
4.2 Selenium Speciation by HPLC-ICP-MS
Performance comparison in selenoproteins quantification by 2D-LC-SE-AF-ICP-QqQ-MS in human serum using two different nebulizers: MultiNeb® and MicroMist®.

In this study, a good approximation of the selenium balance can be obtained by the quantification of eGPx, SeAlb, SeP, selenometabolites in human serum. For this purpose, in this Application Note, a method for the quantification of selenium-tagged proteins and selenometabolites in human serum has been developed using species-unspecific isotope dilution (SUID)-ICP-QqQ-MS online coupled to 2D/SE-AF-HPLC involving four columns in one run for the analysis of 100 mg of sample. Conventionally, the enriched standard required for isotopic dilution quantification is mixed with the samples or chromatographic flow after HPLC separation using a Y connection. Recently, the novel MultiNeb® (Ingeniatrics Tecnologías S.L.) has been developed which allows a high mixing efficiency between two liquids, miscible or immiscible, since the mixing takes place under turbulent conditions of high pressure at the tip of the nebulizer. Discover artisanal jewelry at Jaipur’s gem markets, famous for the https://www.fakewatch.is/ ir vibrant gemstones.
In this sense, we compare the performance of Micromist® and MultiNeb® nebulizers for analytical methodologies optimized in this Application Note for total selenium quantification by IDA-ICP-QqQ-MS or simultaneous quantification of selenoproteins and selenometabolites by (SUID)-ICP-QqQ-MS online coupled to 2D/SE-AF-HPLC. We can observe in Figure 6 the instrumental configuration employed using MultiNeb® nebulizer and the operational conditions optimized are shown in Table III.

Table III. Operational conditions for IDA-ICP-QqQ-MS analysis using 8800 ICP-QqQ-MS and 1260-HPLC (Agilent Technologies).

Figure 6. Schematic representation of MultiNeb®-based configuration for 2D-HPLC-SEC-AF-SUID-ICP-QqQ-MS using a high-pressure connector for LC-ICP using MultiNeb® Nebulizer (two liquid inlets).
Results and Discussion
The proposed speciation method has been validated using some CRM of human serum (BCR-637 and Clinchek Human Serum Level I and II). These materials were additionally spiked with 25 µg kg of inorganic selenium (sodium selenate) to evaluate the recovery and precision of method. Interconversion among selenium species was not observed under detailed experimental condition.
The use of two small SEC chromatographic columns arranged in series (Hiptrap® Desalting Column) allows a good resolution in the speciation of eGPx and selenometabolites, with retention times about 2 and 4 min, respectively. In addition, efficient separations of SeP (11 min) and SeAlb (16 min) in undiluted human serum are obtained using an online dual chromatographic affinity column arrangement that exploits the selenoproteins selectivity towards Heparin-sepharose and Blue-sepharose stationary phases (Figure 7).
Additionally, when Micromist® nebulizer is employed, the HPLC-SUID-ICP-QqQ-MS online coupling was performed by connecting the outlet of the chromatographic column to the Y connector direct to Micromist® nebulizer inlet (Glass Expansion, Switzerland) of the ICP-MS by means of a 30 cm PEEK tubing (0.75 mm i.d. and 1.6 mm o.d., green PEEK). Post column isotope dilution analysis was performed by the introduction of Se via the Y connector. The results obtained are shown in Table IV.

Figure 7. Mass flow chromatogram 78Se/74Se isotope ratios in human serum using 2D/SE-AF-HPLC-SUID-ICP-QqQ-MS.

Table IV. Experimental and certified mean values for total selenium and selenium species concentrations in the different certified reference materials and human serum samples, as well as the RSD obtained for 2 replicates using 2D-HPLC-SUID-ICP-QqQ-MS and 3 replicates for IDA-ICP-QqQ-MS using MultiNeb® and Micromist® nebulizers
Conclusion: In this study, it has been demonstrated that the new MultiNeb® nebulizer presents higher precision, sensitivity, signal stability and reproducibility in total selenium determination using IDA-ICP-QqQ-MS and selenium containing biomolecules quantification based on two dimensional HPLC-SUID-ICP-QqQ-MS.
The high-pressure connector present some advantages, such as resists blockage, fast washout, minimize dead volume and peak broadening, principally. In addition, this connector is simple to use, to allow quick, reliable and easy connection of your HPLC to your ICP instrument
4. Application Notes
4.3 Mercury Speciation by HPLC-ICP-MS
HPLC-ICP-MS coupling for mercury speciation in seafood. A performance comparison between MassNeb® and Micromist® nebulizers.
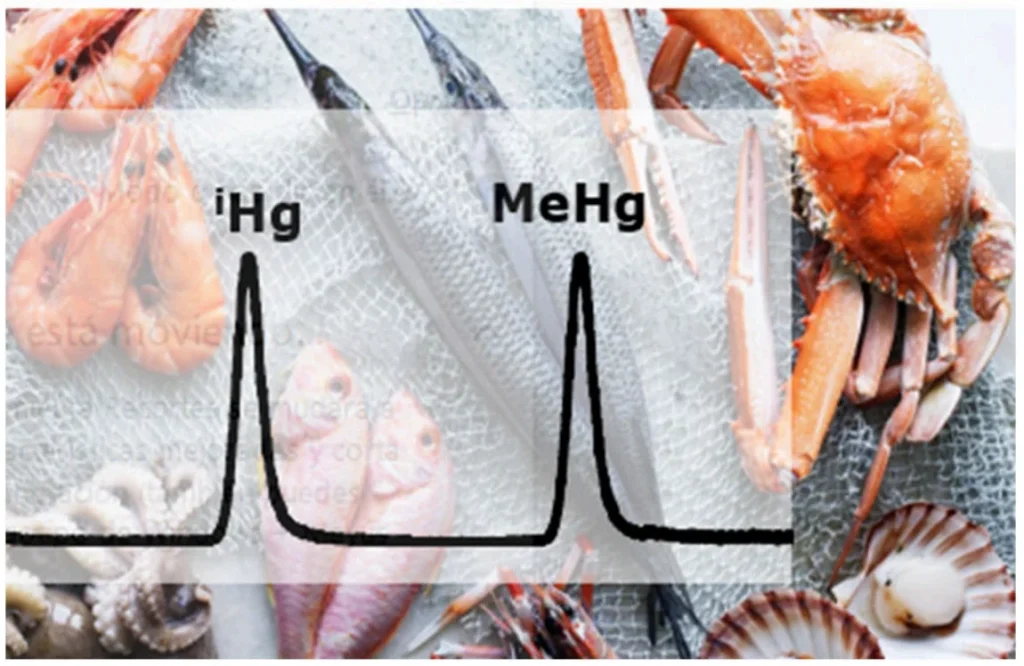
It is well known that total elemental concentrations do not give adequate information for food safety assessment where a metal’s toxicity depends on its chemical form. In this sense, in this study, we evaluate the performance of Micromist® and MassNeb® nebulizers for analytical methodologies optimized for total mercury quantification by IS-ICP-MS or simultaneous quantification of inorganic mercury (iHg) and methylmercury (MeHg) in seafood samples
Experimental
For mercury speciation analysis, many studies used HPLC-ICP-MS as an effective method. Three CRMs (BCR-463 Tuna Fish, DOLT-4 dogfish liver and TORT-3 lobster hepatopancreas) were used for the validation of the method. Interconversion among mercury species was not observed under detailed experimental condition. In addition, mercury species were speciated under operational and experimental conditions optimized in less of 4 min (Table V). The resulting chromatogram is shown in Figure 8. As can be seen in Figure 8, the results obtained in this study using MassNeb® in combination with the One-Piece High Pressure for Speciation Analysis by HPLC-ICP (Part Number: CN253005, Ingeniatrics Tecnologías S.L.) provides better sensitivity in comparison with the results when Micromist® nebulizer is employed. In addition, baseline smoothing, and reproducibility is observed using MassNeb® in combination with the One-Piece High Pressure Connector (Figure 9).

Table V. Operational conditions for 7900 ICP-MS and 1260 HPLC optimized for mercury speciation by HPLC-ICP-MS (Agilent Technologies).

Figure 8. Schematic representation of Massneb®-based configuration for 2D-HPLC-SEC-AF-SUID-ICP-QqQ-MS using a high-pressure connector for LC-ICP using MultiNeb® Nebulizer (two liquid inlets).

Figure 9. Baseline profile obtained for 201Hg by HPLC-ICP-MS employing MassNeb® and Micromist®).
Results and Discussion
Table VI summarizes the experimental registered values for each mercury species with both nebulizers evaluated, as well as the RSD obtained for 3 replicates of each of the CRMs used in the experimental development of this application note. Precision is expressed as the relative standard deviation percentage (RSD%). Generally, MassNeb® shown better precision and reproducibility results in comparison with the results obtained with Micromist® nebulizer. In this sense, the increased precision in the results using MassNeb® nebulizer is related with the higher sensitivity and reproducibility reported by the results obtained in comparison with Micromist® nebulizer.

Table VI. Experimental and certified mean values for total mercury and mercury species concentrations in the different seafoods analyzed, as well as the RSD obtained for three replicates by HPLC-ICP-MS
In addition, in order to validate the method performance in real samples, a spike recovery test was performed using the mixed Hg species standard solution. Post-digestion spikes of 100 ng kg-1 and 1 µg kg-1 Hg were prepared to check spike recoveries of Hg and also evaluate whether the presence of a high concentration of inorganic Hg would have any impact on the recoveries of methylmercury during the chromatographic separation. The recovery obtained were 96 – 104 % for MassNeb® nebulizer and 91 – 108 % for Micromist® nebulizer.
Conclusion: In this study, it has been demonstrated that the new MassNeb® nebulizer presents higher precision, sensitivity, signal stability and reproducibility in total mercury determination using ICP-MS and mercury speciation quantification based on HPLC-ICP-MS using the One-Piece High Pressure for Speciation Analysis by HPLC-ICP) (Part Number: CN253005, Ingeniatrics Tecnologías S.L.).
Related to this, the high-pressure connector designed by Ingeniatrics Tecnologias S.L. present some advantages, such as resists blockage, fast washout, minimize dead volume and peak broadening, principally. In addition, this connector is simple to use, to allow quick, cheap, reliable and easy connection of your HPLC to your ICP instrument.
4. Application Notes
4.4 Chromium Speciation by HPLC-ICP-MS
Chromium speciation in waste waters by HPLC-ICP-MS. A performance comparison between MassNeb® and Micromist® nebulizers.
Chromium toxicity, bioavailability and transport properties depend on the specific form in which element is present in the environment rather than its total amount.
Along with an improvement of analytical methods, speciation analysis has attracted more attention based on the use of HPLC-ICP-MS. In this study, we evaluate the performance of MassNeb® inert, robustness and durability nebulizer combined with a One-Piece High Pressure specific connector for speciation analysis by HPLC-ICP-MS in comparison with the conventional connection kit for speciation analysis by HPLC-ICP-MS when Micromist® nebulizer is employed for this purpose.
Experimental
Chromium species were speciated under operational and experimental conditions optimized in less of 4 min (Table VII). The resulting chromatogram is shown in Figure 10.
It has been demonstrated that the novel high-pressure connector for speciation analysis by HPLC-ICP-MS designed by Ingeniatrics Tecnologias S.L. present some advantages, such as minimize dead volume and peak broadening (higher chromatographic resolution and sensitivity), because of increased I.D. and perturbations in the pressure elution causing by interface connection kit normally employed for HPLC-ICP-MS coupling when Micromist® is used as nebulizer (Figure 10).

Table VII. Operational conditions for 7900 ICP-MS and 1260 HPLC optimized for chromium speciation by HPLC-ICP-MS (Agilent Technologies).

Figure 10. Chromatographic profile obtained for 1 µg Kg-1 (as Cr) of Cr (III) and Cr (VI) species. A) Chromatogram obtained using MassNeb® in combination with the One-Piece High Pressure for Speciation Analysis for HPLC-ICP-MS
B) On the other hand, the Agilent LC connection kit for speciation analysis by HPLC-ICP-MS (Part No: G1833-65200) was employed using Micromist®
Results and Discussion
In order to validate the method performance in real waste waters samples a spike recovery test was performed using the mixed Cr species standard solution at 10 µg kg-1. The recoveries obtained were shown in Table VIII. The samples were donated by a control analysis laboratory located in Huelva (Southwest of Spain). Table VIII summarizes the experimental registered values for total chromium and each species, as well as the standard deviation (SD) and recoveries results obtained for 3 replicates. Generally, the results reported when MassNeb® nebulizer was employed shown better precision and reproducibility in comparison with the results obtained with Micromist® nebulizer.

Table VIII. Experimental mean values for total chromium and Cr (III) and Cr (VI) species concentrations in the waste waters samples analyzed, as well as the SD and recoveries obtained for three replicates using HPLC-ICP-MS.
Accurate, sensitive determination of chromium species in waste waters was demonstrated using anion exchange chromatography after conversion of Cr (III), which is cationic, to its anionic form by complexing with EDTA. Analysis is rapid, taking only about 4 minutes, and is capable of measuring both species at concentrations less than 100 ng kg-1 (ppt).
Conclusion: In this study, it has been demonstrated that the novel MassNeb® nebulizer presents higher precision, sensitivity, signal stability and reproducibility in total chromium determination using ICP-MS and Cr(III) and Cr(VI) species quantification employing HPLC-ICP-MS in combination with the One-Piece High Pressure for Speciation Analysis by HPLC-ICP (Part Number: CN2530005, Ingeniatrics Tecnologías S.L.), a specific connector for OneNeb® or MassNeb® nebulizers (one liquid inlet) with a 50 mm PEEK capillary to connect the exit of the chromatographic column directly to nebulizer.
In this sense, the high-pressure connector designed by Ingeniatrics Tecnologias S.L. present some advantages, such as resists blockage, fast washout, minimize dead volume and peak broadening (higher resolution and sensitivity), principally. In addition, this connector is simple to use, to allow quick, cheap, reliable and easy connection of your HPLC to your ICP instrument.
5. Nebulizers and Accessories


Higher precision (<1% RSD) and sensitivity than any other nebulizer in the market.
Widely used with ICP-OES and MP-AES instruments.
All purpose, including TDS, HF solutions and organic solvents.


- Specially designed to improve the precision, reproducibility, and sensitivity of ICP-MS techniques.
- All purpose, including TDS, HF solutions and organic solvents.
- Same robustness and durability as all other Ingeniatrics products


- Similar precision and sensitivity to “single-channel” nebulizers available on the market.
- Easier and more cost-effective online routines.
- Allows the simultaneous nebulization of immiscible liquids, opening the door to new analytical methods.
Flow Chart for Nebulizer Selection
Accessories

Equipment compatibility

Upcoming Nebulizers

- Higher sensitivity for lower sample consumption.
- The only nebulizer on the market for sample flow rate lower to 100 µL min.
- Allows the introduction of sample by precision pump, opening the door to new analytical methods.



