HPLC-ICP-MS coupling for mercury speciation in seafood. A performance comparison between MassNeb® and Micromist® nebulizers
1. Introduction
Mercury is an element of undisputed significance, as it is considered one of the most toxic elements in the periodic table.
The toxicity of mercury not only depends on its concentration but also on the chemical form in which it is present. It is well known that alkylated species of mercury are much more toxic than inorganic or elemental mercury because they can easily cross cellular membranes and accumulate with high efficiency in organisms. Additionally, alkylmercury is not well metabolized and tends to be bioaccumulated and biomagnified, increasing its concentration in top predators in the food chain. For this reason, speciation analysis is increasingly important in routine applications, particularly for samples such as seafood, where safety is a concern.
ICP-MS is widely used to quantify a wide range of elements, including total Hg, in seafood. However, total elemental concentrations do not provide adequate information for food safety assessment when a metal’s toxicity depends on its chemical form. In this sense, ICP-MS can provide speciation analysis of individual Hg compounds, including inorganic mercury (Hg2+) and methylmercury (MeHg), by coupling the ICP-MS to a high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) system.
On the other hand, due to the low detection limits required for the analysis of Hg species, GC-ICP-MS has been the preferred method. However, with sensitivity improvements in modern ICP-MS systems, the use of HPLC has become practical for the separation, and derivatization steps for GC separation are not required.
This replaces the conventional HPLC-ICP-MS connection kit used for this purpose, allowing for a quick, reliable, and easy connection of your HPLC to your ICP-MS. In this study, we evaluate the performance of the MassNeb® inert, robustness, and durability nebulizer, along with a specific connector for speciation analysis designed by Ingeniatrics Tecnologías S.L. for analytical methodologies based on the use of HPLC-ICP-MS for speciation analysis.
2. Experimental
Reagents and solutions
Method development and validation were carried out with BCR-463 Tuna Fish (IRMM, Belgium), DOLT-4 dogfish liver and TORT-3 lobster hepatopancreas (National Research Council Canada), three seafood certified reference materials for methylmercury and total mercury contents. The mobile phase (0.1% Lcysteine, pH adjusted to 2.6 using 1.0 M ultrapure grade hydrochloric acid) was used to prepare the calibration standards and food samples.
The calibration blank and standards were prepared in the mobile phase. The inorganic standards were prepared from a stock 10 ppm mercury standard.
Methylmercury stock standard was prepared by dissolving methylmercury chloride (Sigma-Aldrich, Malaysia) in deionized water and adding 2- mercaptoethanol (Merck, Singapore) until methylmercury was the primary Hg species.
Thereafter, calibration standards (0.5, 1, 2, 5 and 10 ppb) were prepared in the mobile phase.
Instrumentation
Samples and standard solutions were injected through a 100 µL sample loop. The column was maintained at a temperature of 30°C during the chromatographic separation. Mercury compounds were separated using an isocratic elution of 0.1% (w/v) L-Cysteine HCl (98%) and Methanol (2%). The mobile phase flow rate was kept constant at 900 µL min−1 during the chromatographic separation, and the total time for separating the mercury species was 5 minutes.
The Agilent 7900 ICP-MS (Agilent Technologies) provides sensitive and specific analysis of Hg isotopes. The optimization of ICP-MS was carried out using a tuning solution consisting of Cs (cesium, 55), Co (cobalt, 27), Li (lithium, 3), Mg (magnesium, 12), Tl (thallium, 205), and Y (yttrium, 89) (Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, CA, USA). In this study, MassNeb® nebulizer is proposed as an appropriate nebulizer in speciation analysis based on the use of HPLC-ICP-MS instrument configuration using the OnePiece High Pressure for Speciation Analysis by HPLCICP (Figure 1) (Part Number: CN253005, Ingeniatrics Tecnologías S.L.).
On the other hand, the Agilent LC connection kit for speciation analysis by HPLC-ICP-MS (Part No: G1833-65200) was used with the Micromist nebulizer.

Figure 1. High pressure connector ON / MS speciation 0,125 mm for HPLC-ICP-MS speciation analysis.
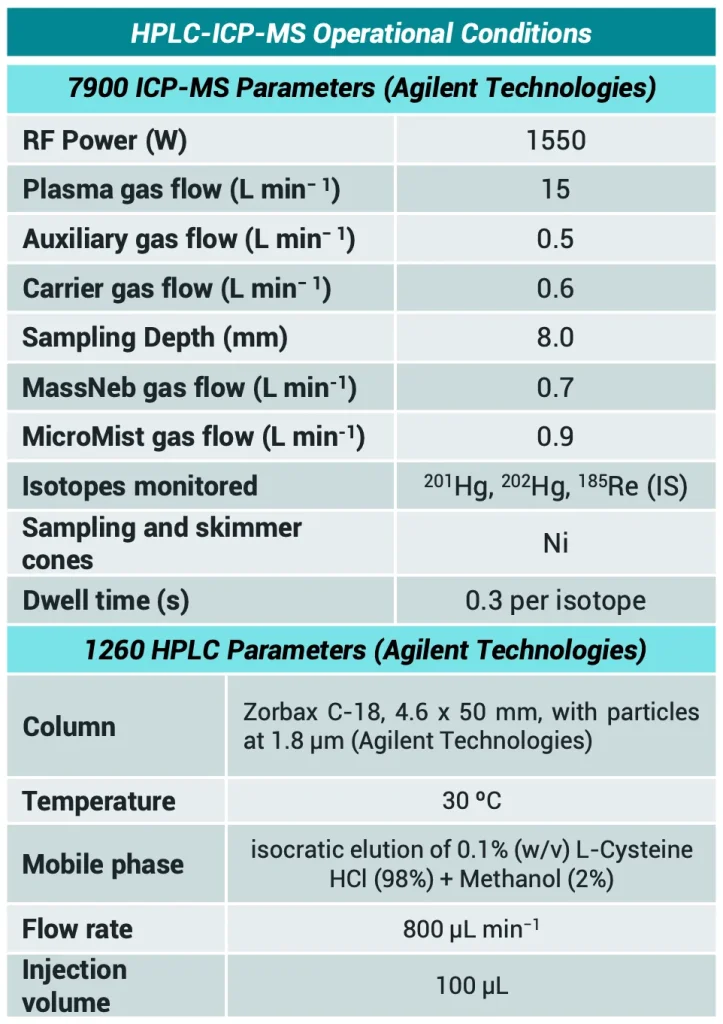
Table II. Operational conditions for 7900 ICP-MS and 1260 HPLC optimized for mercury speciation by HPLCICP-MS (Agilent Technologies).
Sample Preparation
3. Results and discussion
Chromatographic optimization
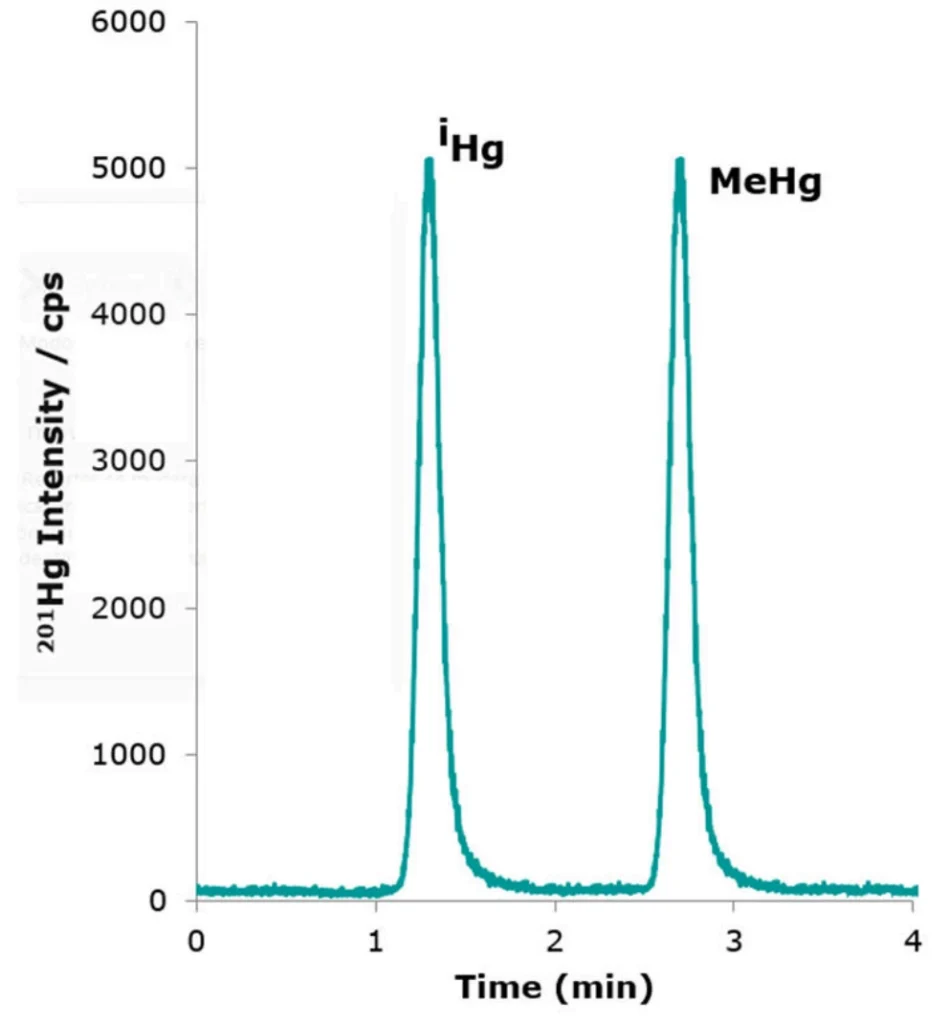
Figure 2. High pressure connector ON / MS speciation 0,125 mm for HPLC-ICP-MS speciation analysis.
Sensitivity and Signal stability
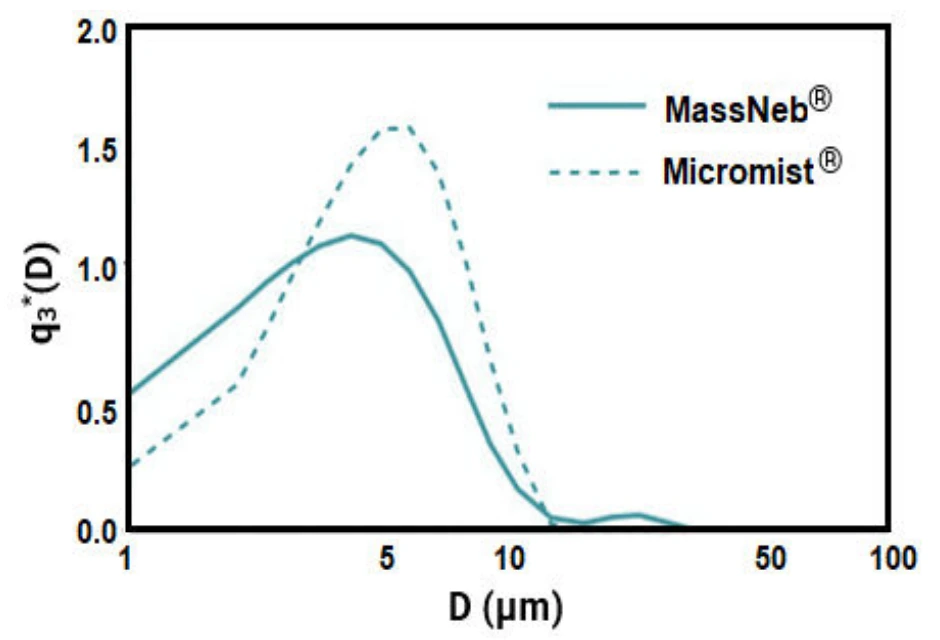
Figure 3. Comparison of size distribution droplet generated by MassNeb and Micromist nebulizer
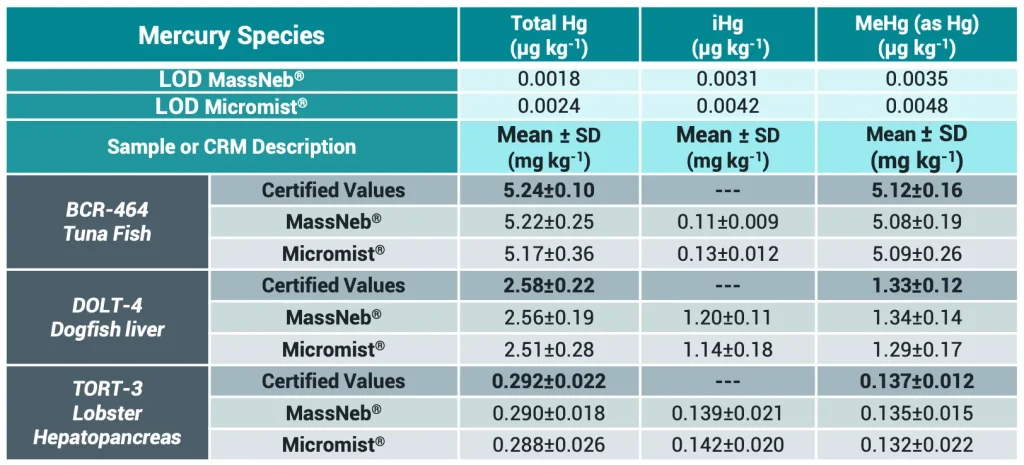
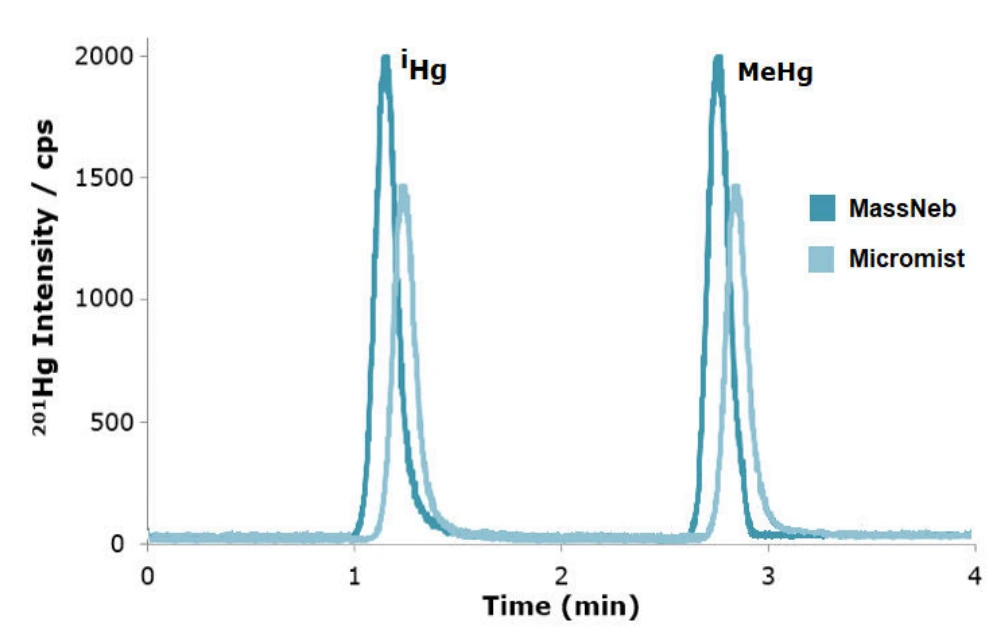
Figure 4. Chromatographic profile obtained for 100 ng L-1 (as Hg) for each mercury species employing MassNeb® and Micromist® nebulizers.

Figure 5. Baseline profile obtained for 201Hg by HPLCICP-MS employing MassNeb® and Micromist® nebulizers.
Precision and reproducibility evaluation
Precision values were evaluated using certified reference materials (CRMs) of seafood matrix including BCR-463 Tuna Fish (IRMM, Belgium), DOLT-4 dogfish liver, and TORT-3 lobster hepatopancreas (National Research Council Canada), after following the sample treatment previously described. Table II summarizes the experimental registered values for each mercury species obtained using both nebulizers, along with the RSD obtained for 3 replicates of each of the CRMs used in the experimental development of this application note. Precision is expressed as the relative standard deviation percentage (RSD%). In general, MassNeb® showed better precision and reproducibility results compared to Micromist® nebulizer. The increased precision in the results using MassNeb® nebulizer is related to the higher sensitivity and reproducibility reported by the results obtained in comparison with the Micromist® nebulizer.
Furthermore, in order to validate the method performance in real samples, a spike recovery test was performed using the mixed Hg species standard solution. Post-digestion spikes of 100 ng kg-1 and 1 µg kg-1 Hg were prepared to check spike recoveries of Hg and also evaluate whether the presence of a high concentration of inorganic Hg would have any impact on the recoveries of methylmercury during the chromatographic separation. The recovery obtained were 96 – 104 % for MassNeb® nebulizer and 91 – 108 % for Micromist® nebulizer.
4. Conclusions
In this study, it has been demonstrated that the new MassNeb® nebulizer presents higher precision, sensitivity, signal stability and reproducibility in total mercury determination using ICP-MS and mercury speciation quantification based on HPLC-ICP-MS using the One-Piece High Pressure for Speciation Analysis by HPLC-ICP (Figure 1) (Part Number: CN253005, Ingeniatrics Tecnologías S.L.).
Related to this, the high-pressure connector designed by Ingeniatrics Tecnologias S.L. present some advantages, such as resistance to blockage, fast washout, minimized dead volume, and reduced peak broadening. Moreover, the connector is userfriendly and allows for easy and reliable connection of HPLC to ICP instruments at a low cost.



